- UPSC LABS
- February 8, 2025
- 6:35 pm
- Ratings: ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
The concept of Light Years, recent space missions and discoveries
The interplay of space and time forms the bedrock of our understanding of the universe. From measuring vast cosmic distances in light years to exploring celestial bodies through cutting-edge missions, humanity’s quest to solve the cosmos has reshaped science, technology, and philosophy. This article explores the concept of light years, recent breakthroughs in space exploration, and their implications for aspirants preparing for competitive examinations like the UPSC Civil Services.
Table of Contents
Understanding Light Years and Cosmic Distances
The term “light year” is fundamental to astronomy, yet its significance is often underestimated. A light year is the distance light travels in one year, approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers or 5.88 trillion miles. Since light speed in a vacuum is constant (~299,792 km/s), this unit provides a reliable metric for gauging astronomical distances. Unlike kilometers or miles, which are impractical for interstellar scales, light years contextualize the universe’s enormity. For instance, the nearest star system, Alpha Centauri, is 4.3 light years away, while the Milky Way spans 100,000 light years in diameter.
The choice of light years as a measurement unit stems from the universal constancy of light speed, a cornerstone of Einstein’s theory of relativity. This constancy ensures that distances calculated using light years remain consistent despite cosmic phenomena like gravitational lensing or the universe’s expansion. For example, gravitational lensing—where massive objects bend light—alters light’s path, not speed, making light years a stable reference.
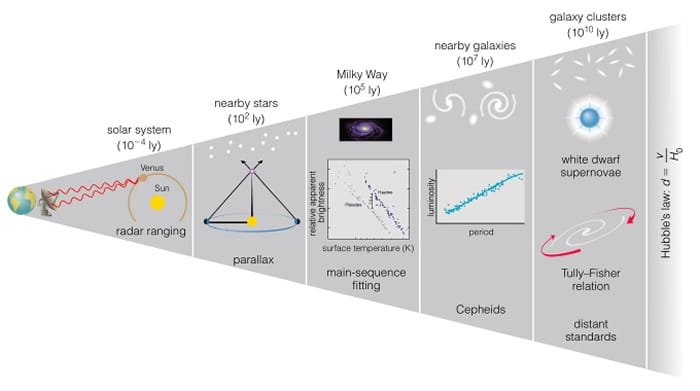
The cosmic distance ladder—a hierarchy of measurement techniques—further refines these calculations. It combines parallax (for nearby stars), standard candles like Cepheid variables (for galaxies), and redshift (for distant galaxies) to map the universe. Light years, parsecs (3.26 light years), and megaparsecs (million parsecs) collectively form this ladder, enabling astronomers to measure objects billions of light years away.
Space Missions: Expanding Horizons
Modern space missions blend technological innovation with scientific curiosity, targeting celestial bodies from the Moon to distant asteroids. These missions advance knowledge and inspire geopolitical collaboration and economic opportunities.
Lunar Exploration:
The Moon remains a focal point for missions aiming to establish a sustainable human presence. In 2024, China’s Chang’e 6 mission retrieved samples from the Moon’s far side, offering insights into its geological history. In 2025, NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) will deploy landers like Astrobotic’s Griffin-1 and Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C to analyze lunar soil, test oxygen extraction technologies, and prepare for the Artemis mission. Japan’s M2/Resilience Mission (January 2025) will study lunar water resources, a critical step for future colonies.
Planetary and Asteroid Missions:
⦿ Europa Clipper: Launched in 2024, this NASA mission will reach Jupiter’s moon Europa by 2030, investigating its subsurface ocean for potential life.
⦿ Lucy Mission: After visiting the asteroid Donaldjohanson in 2024, Lucy will proceed to Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids in 2025, unraveling clues about the solar system’s formation.
⦿ Tianwen-2: China’s 2025 mission aims to return samples from asteroid Kamoʻoalewa, advancing planetary defense and mining prospects.

Telescopes and Observatories:
⦿ SPHEREx: Launching in February 2025, this NASA observatory will map 450 million galaxies in near-infrared, studying galaxy evolution and cosmic water distribution.
⦿ Euclid Space Telescope: Operational since 2023, Euclid is mapping dark matter and energy. Its recent discovery of a rare Einstein ring around galaxy NGC 6505 exemplifies its potential to study gravitational lensing at unprecedented scales.
Recent Discoveries in Space Science
2023–2025 has witnessed groundbreaking discoveries that redefine our cosmic understanding.
Einstein Ring Around NGC 6505:
In September 2023, the Euclid Space Telescope detected a near-perfect Einstein ring around the galaxy NGC 6505, located 590 million light years away. This phenomenon occurs when a foreground galaxy’s gravity bends light from a background galaxy (4.42 billion light years distant) into a luminous ring. Such rings are rare (less than 1% of galaxies exhibit them) and serve as cosmic laboratories to study dark matter, universe expansion, and galaxy formation.
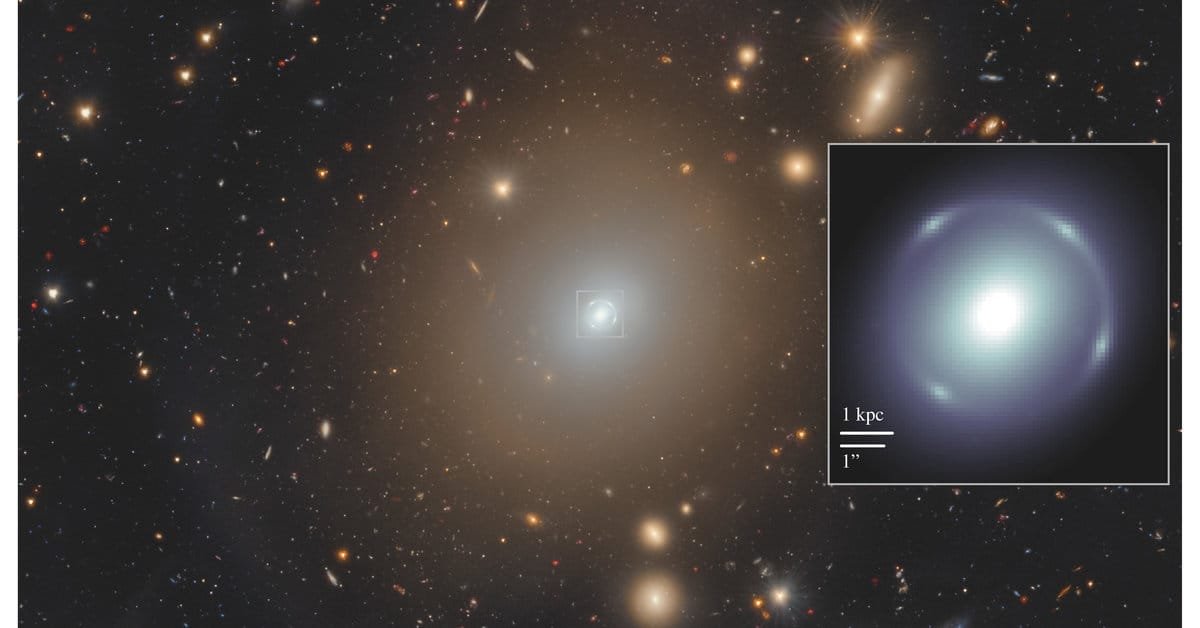

Dark Matter and Dark Energy Insights:
Einstein rings and weak gravitational lensing data from Euclid are shedding light on dark matter (27% of the universe) and dark energy (68%), invisible components driving cosmic expansion. By analyzing lensing distortions, scientists map dark matter’s distribution and test theories about dark energy’s repulsive force.
Exoplanets and Habitability:
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) continues studying exoplanets like K2-18b, where potential biosignatures suggest habitable conditions. Such findings align with UPSC topics on astrobiology and the search for extraterrestrial life.
Implications for UPSC Preparation
Space science is a recurring theme in UPSC exams, emphasizing conceptual clarity and current affairs integration.
Key Topics:
⦿ Light Years and Measurement: Understand why light years are preferred over terrestrial units (e.g., 2021 UPSC Prelims question).
⦿ Gravitational Lensing: Relate it to dark matter, Einstein’s relativity, and phenomena like Einstein’s rings (2018 Prelims question).
⦿ Space Missions: Focus on milestones like Gaganyaan (India’s crewed mission), CLPS, and international collaborations (e.g., NISAR satellite with NASA).
⦿ Cosmology: Big Bang theory, dark energy, and universe expansion are critical for the mains answers.
Recent Developments:
⦿ ISRO’s 2025 Missions: Gaganyaan’s uncrewed test, NVS-02 navigation satellite, and the NISAR Earth observatory underscore India’s technological prowess.
⦿ Private Space Sector: SpaceX’s Starship and Astrobotic’s lunar missions highlight the growing role of commercial entities in space exploration.
Conclusion
The concepts of space, time, and light years are not merely academic—they are windows into humanity’s place in the cosmos. Recent missions and discoveries, from Einstein rings to lunar sample returns, exemplify the synergy between curiosity and innovation. For UPSC aspirants, mastering these topics requires connecting foundational physics with contemporary advancements, ensuring a holistic grasp of both science and its societal impact. As we venture further into the universe, the lessons learned will undoubtedly shape policies, technologies, and philosophies for generations to come.
