- UPSC LABS
- February 8, 2025
- 6:35 pm
- Ratings: ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Cosmic inflation and the CDM Lambda Model
The Cosmic Inflation Theory and the Lambda-CDM Model are two of the most significant frameworks in modern cosmology. They provide profound insights into the origin, evolution, and structure of the universe. For UPSC aspirants, understanding these concepts is essential not only for the Science & Technology syllabus but also for developing a holistic perspective on the universe’s mysteries. This essay explores both theories, their interconnections, and their relevance to UPSC preparation.
Table of Contents
Cosmic Inflation Theory: The Universe's Rapid Expansion
The Cosmic Inflation Theory, proposed by Alan Guth in the 1980s, explains the universe’s exponential expansion in the first fraction of a second after the Big Bang. Key aspects include:
Key Features:
✎ Rapid Expansion: The universe expanded faster than the speed of light in the first 10−3610−36 to 10−3210−32 seconds.
✎ Flattening of the Universe: Inflation explains why the universe appears flat and homogeneous on large scales.
✎ Seeding Cosmic Structures: Quantum fluctuations during inflation seeded the formation of galaxies and galaxy clusters.
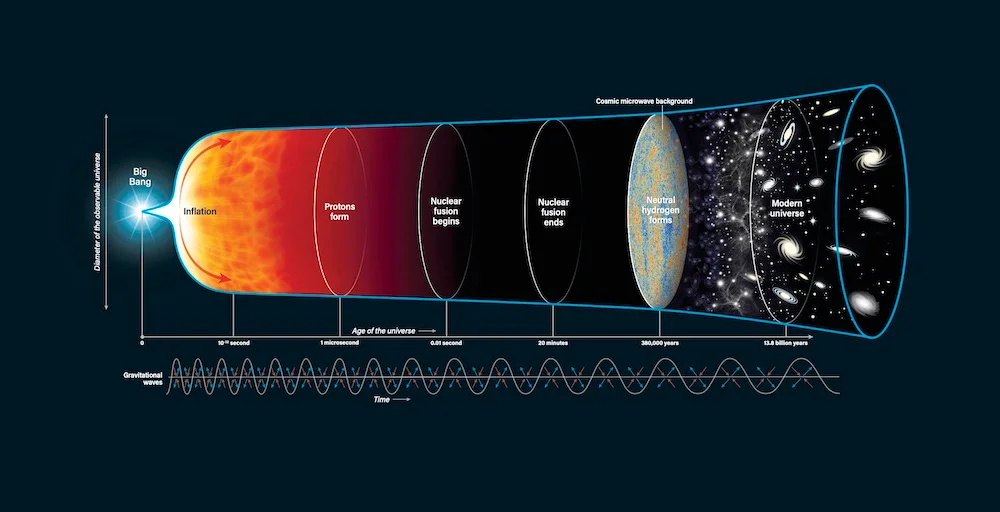
Evidence Supporting Inflation:
✎ Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB): Tiny temperature fluctuations in the CMB align with predictions of inflation.
✎ Large-Scale Structure: The distribution of galaxies and galaxy clusters matches inflationary models.
Why It Matters for UPSC?
✎ Scientific Temper: Demonstrates how theoretical predictions are tested through observations.
✎ Interdisciplinary Linkages: Connects physics, mathematics, and observational astronomy.
✎ Current Affairs: Ongoing experiments like the James Webb Space Telescope and CMB observations continue to test inflation.
Lambda-CDM Model: The Standard Model of Cosmology
The Lambda-CDM Model is the prevailing framework for understanding the universe’s composition and evolution. It combines two key components:
✎ Lambda (Λ): Represents dark energy, responsible for the universe’s accelerated expansion.
✎ CDM (Cold Dark Matter): Explains the gravitational effects shaping the universe’s large-scale structure.
Key Features:
✎ Dark Energy (68%): Drives accelerated expansion.
✎ Dark Matter (27%): Provides gravitational scaffolding.
✎ Ordinary Matter (5%): Includes stars, planets, and galaxies.
Timeline of the Universe:
✎ Big Bang: The universe begins in a hot, dense state.
✎ Inflation: Rapid expansion flattens and homogenizes the universe.
✎ Structure Formation: Dark matter clumps form galaxies and galaxy clusters.
✎ Dark Energy Dominance: Accelerated expansion begins ~5 billion years ago.
Evidence Supporting the Lambda-CDM Model:
✎ CMB Observations: Match predictions of the model.
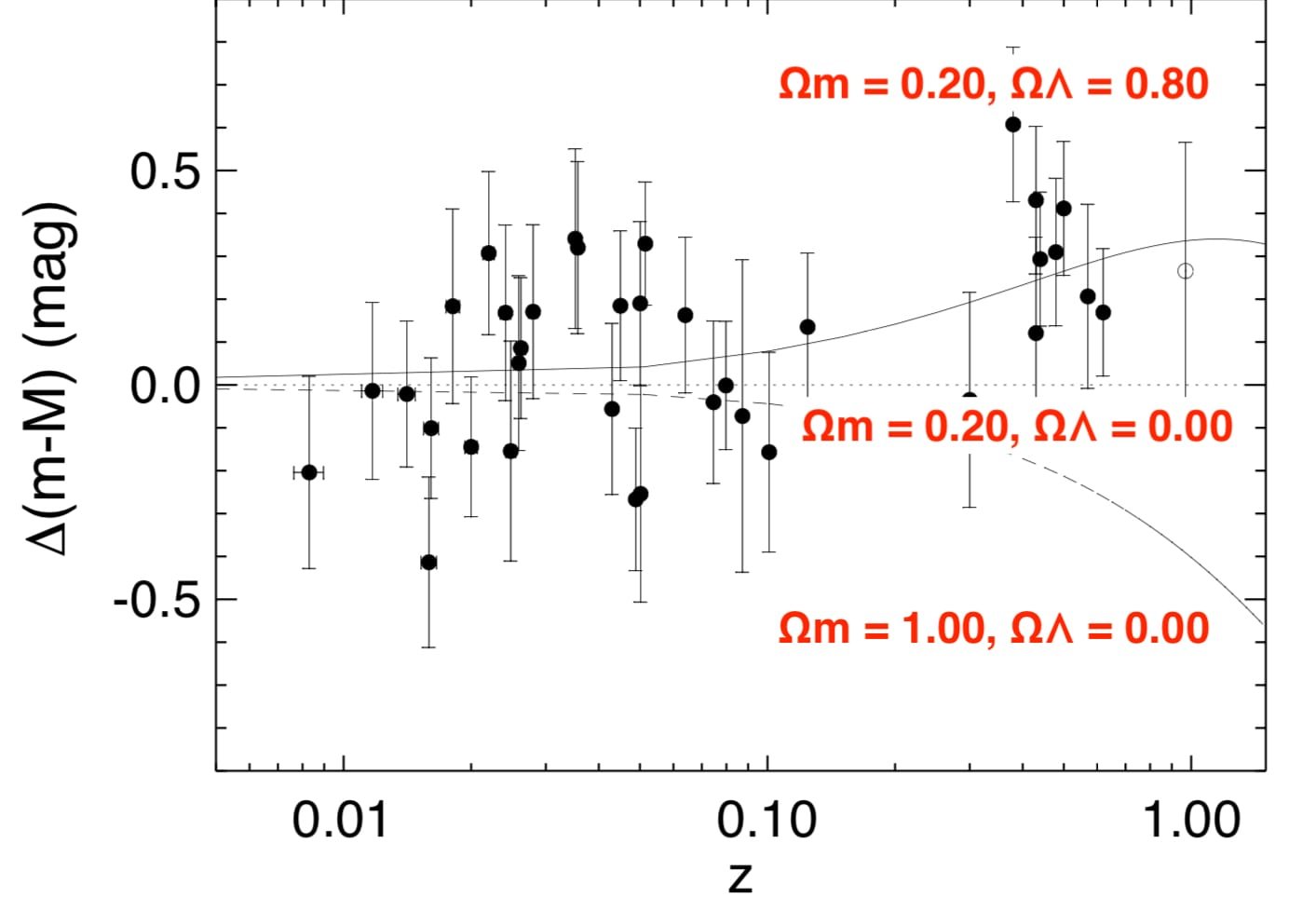
✎ Supernova Surveys: Confirm the accelerated expansion of the universe.
✎ Galaxy Surveys: Reveal the large-scale structure shaped by dark matter.
Why It Matters for UPSC?
✎ Science & Technology: Core concepts like dark energy, dark matter, and the Big Bang are frequently tested.
✎ Geography: Understanding the universe’s structure and evolution is part of the physical geography syllabus.
✎ Essay Topics: Themes like “The universe is not only stranger than we imagine but stranger than we can imagine” or “Science as a tool to unravel cosmic mysteries.
Interconnection Between Inflation and the Lambda-CDM Model
✎ Inflation as the Starting Point: Inflation sets the initial conditions for the Lambda-CDM Model, explaining the universe’s flatness and homogeneity.
✎ Dark Matter and Dark Energy: Both theories rely on these mysterious components to explain the universe’s structure and expansion.
✎ Observational Synergy: Data from CMB observations, galaxy surveys, and supernova studies support both theories.
