- UPSC LABS
- February 8, 2025
- 6:35 pm
- Ratings: ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Doppler Shift, Gravitational Waves and CMB
The study of the universe involves understanding various phenomena that provide insights into its origin, evolution, and structure. Among these, gravitational waves, the Doppler-shift, and the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation are three critical concepts that have revolutionized our understanding of cosmology and astrophysics. These phenomena are not only fundamental to modern physics but also hold significant relevance for competitive exams like the UPSC, where a multidisciplinary understanding of science and technology is essential.
Table of Contents
Gravitational Waves
Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of spacetime, caused by some of the most violent and energetic processes in the universe. Predicted by Albert Einstein in 1916 as part of his General Theory of Relativity, these waves were first directly detected in 2015 by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO).
⦿ Origin and Detection: Gravitational waves are produced by cataclysmic events such as the merger of black holes, collision of neutron stars, or supernova explosions. These events distort spacetime, sending waves that travel at the speed of light. The mathematical description of gravitational waves comes from Einstein’s field equations.
⦿ Significance: The detection of gravitational waves has opened a new window into the universe, allowing scientists to observe phenomena that are invisible to traditional telescopes. For example, the merger of two neutron stars observed in 2017 (GW170817) provided insights into the origin of heavy elements like gold and platinum through nucleosynthesis.
⦿ Applications: Gravitational waves help test the limits of General Relativity, study the properties of black holes, and explore the early universe. They are also crucial for understanding the dark energy driving the accelerated expansion of the universe. The LIGO-India project, set to become operational in the 2030s, will enhance global efforts in gravitational wave astronomy.
Doppler Shift
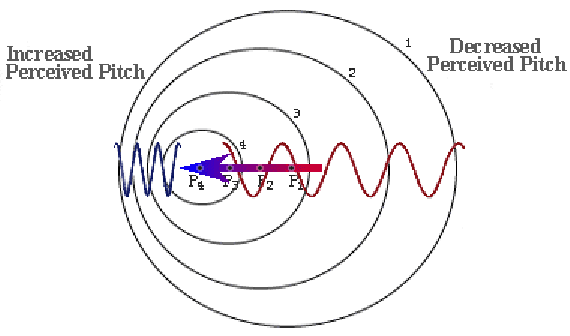
The Doppler shift, or Doppler effect, is the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. This phenomenon is fundamental to both astronomy and cosmology, as it helps measure the motion of celestial objects.
⦿ Redshift and Blueshift: When an object moves away from an observer, its light shifts to longer wavelengths, known as redshift. Conversely, when an object moves closer, its light shifts to shorter wavelengths, called blueshift.
⦿ Applications in Astronomy: The Doppler shift is used to determine the velocity of stars, galaxies, and even exoplanets. For instance, the radial velocity method detects exoplanets by measuring the wobble of a star caused by the gravitational pull of an orbiting planet. The Hubble Space Telescope has extensively used this technique to study distant galaxies.
⦿ Cosmological Significance: The redshift of distant galaxies is a key piece of evidence for the Big Bang theory and the expanding universe. It also helps map the large-scale structure of the universe and study the distribution of dark matter. The Hubble’s Law, v=H0⋅dv=H0⋅d, where vv is the velocity, H0H0 is the Hubble constant, and dd is the distance, quantifies the expansion of the universe.

Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) Radiation
The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation is the afterglow of the Big Bang, providing a snapshot of the universe when it was just 380,000 years old. Discovered accidentally in 1965 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, the CMB is one of the strongest pieces of evidence for the Big Bang theory.
⦿ Discovery and Properties: The CMB is a faint glow of microwave radiation that fills the universe, with a temperature of approximately 2.7 Kelvin (-270.45°C). It is remarkably uniform but contains tiny fluctuations (anisotropies) that represent the seeds of all cosmic structures, such as galaxies and galaxy clusters. The Planck satellite and earlier missions like COBE and WMAP have mapped these fluctuations with unprecedented precision.
⦿ Significance in Cosmology: The CMB provides critical insights into the early universe, including its age (13.8 billion years), composition (4.9% ordinary matter, 26.8% dark matter, and 68.3% dark energy), and the rate of expansion. The Friedmann equations, derived from Einstein’s field equations, describe the expansion dynamics.
⦿ Implications for Modern Physics: The CMB helps test theories of inflation, a rapid expansion of the universe just after the Big Bang, and provides clues about the nature of dark matter and dark energy. It also serves as a cornerstone for understanding the large-scale structure of the universe. The Sachs-Wolfe effect and Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAO) are key phenomena observed in the CMB that help explain the distribution of matter in the universe.
Interconnection and Relevance for UPSC
These three phenomena—gravitational waves, the Doppler shift, and the CMB—are interconnected and provide a comprehensive understanding of the universe. Gravitational waves allow us to observe cosmic events directly, the Doppler shift helps measure the motion and expansion of the universe, and the CMB offers a glimpse into the universe’s infancy. Together, they form the backbone of modern cosmology and astrophysics.
From a UPSC perspective, these topics are crucial for both the Prelims and Mains examinations. Questions may focus on their discovery, significance, and applications, as well as their role in shaping our understanding of the universe. Additionally, these concepts often intersect with topics like space technology, scientific advancements, and India’s contributions to global science, such as its involvement in LIGO-India and the AstroSat mission.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gravitational waves, the Doppler shift, and the CMB radiation are not just scientific curiosities but essential tools for exploring the cosmos. They highlight the importance of interdisciplinary research and technological innovation, making them highly relevant for aspirants aiming to excel in competitive exams and contribute to the scientific and technological progress of the nation.
